Greenhouse Gas Monitoring (dissolved CO2)
Greenhouse gas monitoring plays a crucial role in assessing the health of our oceans, with a particular focus on dissolved CO2 levels. This process involves using advanced pCO2 sensors to track and analyze carbon dioxide concentrations, which are integral to marine biogeochemistry and ocean acidification models. By integrating ocean monitoring techniques and precise pCO2 analysis, scientists can better understand the impacts of greenhouse gases on marine ecosystems and contribute to more effective climate strategies.Greenhouse gas monitoring in the ocean, particularly of dissolved CO2, is key to understanding the broader impacts of climate change on marine environments. Greenhouse gas monitoring involves the measurement and analysis of various gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide that are absorbed by the oceans.
Among these, dissolved CO2 plays a pivotal role due to its significant influence on ocean chemistry and its link to phenomena such as ocean acidification.
Effective monitoring of dissolved CO2 is essential for developing an accurate ocean acidification model, supporting marine biogeochemistry research, and informing global climate strategies.
Dissolved CO2 and Ocean Acidification
Dissolved CO2 is a critical component in the study of ocean acidification. As CO2 levels in the atmosphere increase, so does the amount of CO2 absorbed by the oceans, resulting in a decrease in pH levels.
This acidification process alters the carbonate chemistry of seawater, making it more difficult for organisms like corals, mollusks, and some plankton species to build and maintain their calcium carbonate structures.
Monitoring dissolved CO2 levels helps scientists track these changes and develop models to predict the impacts of acidification on marine ecosystems.
Using pCO2 Sensors to Monitor Dissolved CO2
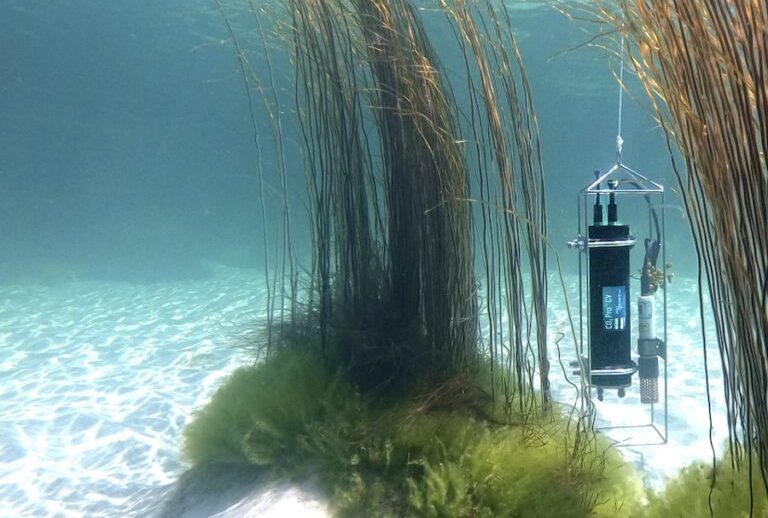
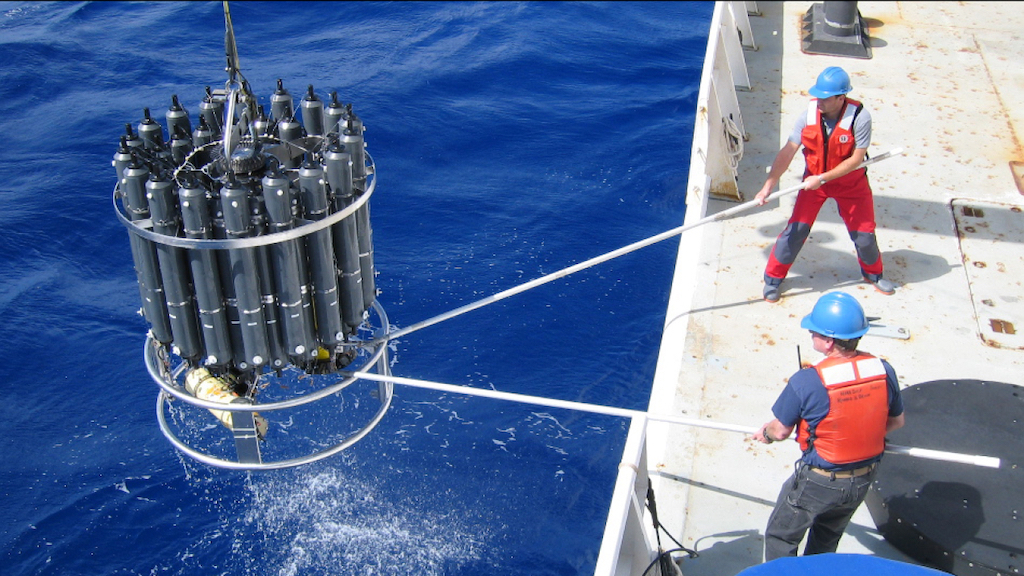
The monitoring of dissolved CO2 in the oceans relies on a variety of advanced tools and technologies. Among these, pCO2 sensors are critical for measuring the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in seawater. These sensors are often deployed on buoys, gliders, and other autonomous platforms, providing continuous data on CO2 levels in different ocean regions.
pCO2 analysis from these sensors allows researchers to assess the spatial and temporal variability of dissolved CO2, offering insights into how different factors, such as temperature, salinity, and biological activity, influence CO2 dynamics in the ocean.
Greenhouse Gas Monitoring Applications in Ocean Monitoring & Marine Biogeochemistry
Greenhouse gas monitoring, with a focus on dissolved CO2, is a key aspect of broader ocean monitoring initiatives. The data gathered from pCO2 sensors and other instruments contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of marine biogeochemistry—the study of chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natural environment.
This information is vital for assessing the health of marine ecosystems and understanding the carbon cycle within the ocean.
Additionally, monitoring dissolved CO2 supports the development of ocean acidification models, which are essential for predicting how marine ecosystems will respond to continued increases in atmospheric CO2 levels.
Challenges in Monitoring Dissolved CO2
The vastness of the ocean and the variability of CO2 concentrations across different regions and depths make comprehensive monitoring a complex task.
Furthermore, the calibration and maintenance of pCO2 sensors in harsh marine environments require meticulous attention to ensure data accuracy and reliability.
Nonetheless, ongoing innovations in sensor technology and deployment strategies are enhancing the ability to monitor greenhouse gases in the ocean more effectively.
Future Directions and Implications for Climate Action
As the impacts of climate change become increasingly apparent, the importance of greenhouse gas monitoring in the ocean is set to grow. Enhanced monitoring capabilities will provide more accurate data on the ocean’s role in the global carbon cycle and the extent of ocean acidification.
This information is critical for informing international climate agreements and strategies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
By integrating data from pCO2 sensors and other monitoring tools, scientists can improve ocean acidification models and provide policymakers with the information needed to mitigate the impacts on marine ecosystems.
Products (9)
Related Articles
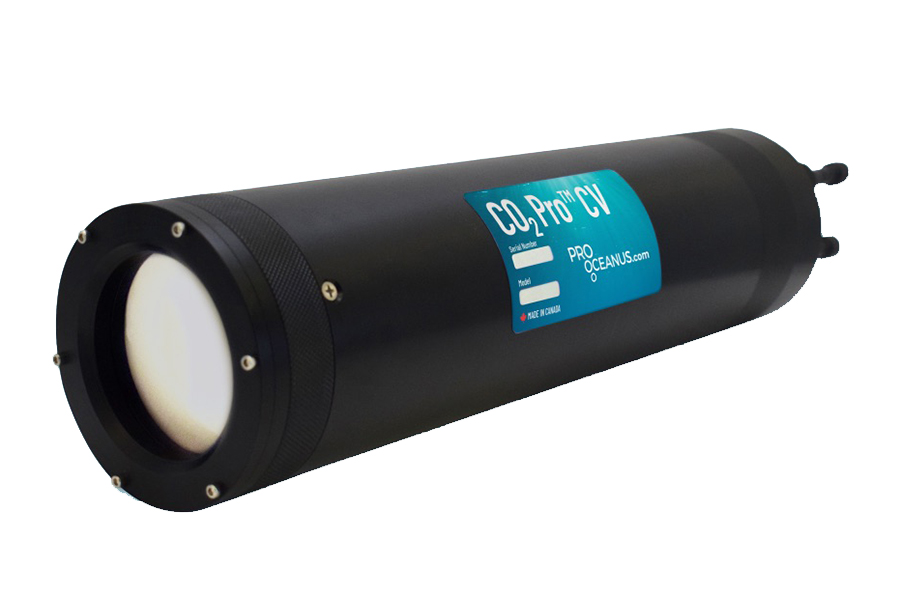

High-Accuracy Dissolved Gas Sensors for Oceanography, Environmental Monitoring, and Oil & Gas Applications
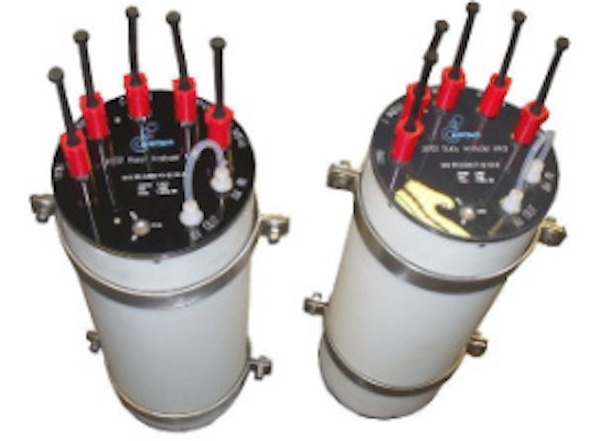

Marine Monitoring Systems for Surface & Underwater Vessels | Advanced Power Solutions for Subsea Vehicles