Methane Analyzers (CH4 Analysis)
A methane analyzer is a sophisticated instrument designed to measure and monitor methane levels in various environments, playing a crucial role in greenhouse gas measurement and analysis. These devices are essential for scientists and researchers focused on understanding methane levels in the atmosphere, a significant factor in climate change studies. Utilizing advanced technology, methane analyzers provide accurate and real-time data, facilitating effective greenhouse gas analysis and aiding in the development of strategies to mitigate methane emissions.A methane analyzer is a specialized instrument designed to detect and quantify the presence of methane (CH₄) gas in various environments. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas, with a global warming potential many times that of carbon dioxide. Accurate monitoring of methane levels is essential across multiple industries, including oil and gas, environmental monitoring, and climate research. In subsea applications, methane analyzers are particularly valuable for detecting methane leaks, monitoring gas hydrates, studying seafloor seepage, and conducting marine geological surveys.
Methane Analyzer Applications
Leak Detection and Monitoring in Oil and Gas Operations
In offshore oil and gas operations, subsea methane analyzers are crucial for detecting leaks from pipelines, subsea wellheads, and other infrastructure. Undetected leaks can lead to significant environmental damage and economic loss. Continuous monitoring systems equipped with methane sensors can alert operators to the presence of leaks, allowing for rapid response and mitigation. These systems are often integrated into autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs) or remotely operated vehicles (ROVs), which survey large areas of the seafloor.
Gas Hydrate Studies
Gas hydrates are crystalline structures that trap methane within a lattice of water molecules. These are commonly found in subsea sediments, particularly in continental margins. Methane analyzers are used in the exploration and monitoring of gas hydrates because they help detect the presence of methane as hydrates decompose, releasing the gas. This is important not only for understanding potential energy resources but also for assessing geohazards and the role of methane in climate change.
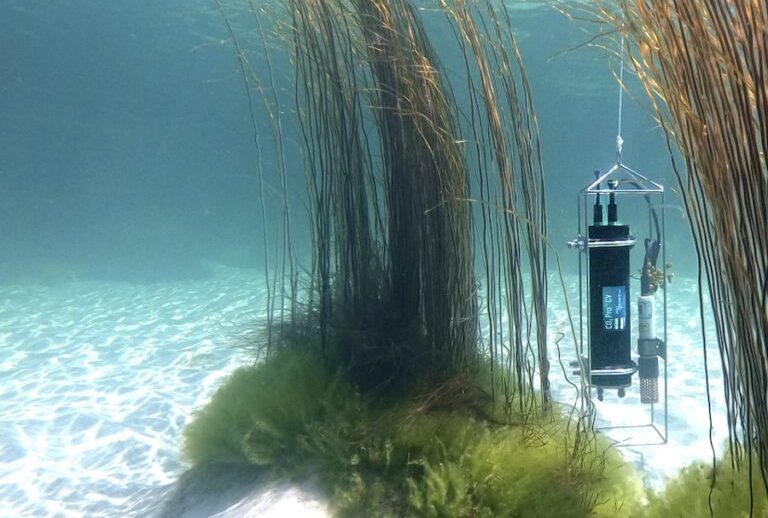
Seafloor Methane Seepage Monitoring
Natural methane seeps are found on the seafloor in various locations, where methane gas escapes from sediment layers into the ocean. Monitoring these seep sites is essential for understanding the carbon cycle and the potential impact on oceanic and atmospheric methane levels. Subsea methane analyzers can be deployed at these seep sites to continuously measure the rate and concentration of methane emissions, providing data for long-term environmental monitoring.
Marine Geological Surveys
In marine geological studies, methane analyzers are used to map gas-rich sediment layers and identify areas of active gas release. When mounted on ROVs or AUVs, these analyzers can cover wide areas, providing real-time data on methane concentrations in the water column. This information is vital for resource exploration, geohazard assessment, and understanding the dynamics of subsea geological formations.
Challenges
Subsea methane analyzers are typically ruggedized to withstand the harsh conditions of deep-sea environments, including high pressure, low temperatures, and corrosive saltwater. They are often integrated into subsea observatories, AUVs, or mooring systems for long-term deployments. Real-time data transmission to surface vessels or shore-based facilities can be achieved through acoustic modems or fiber-optic cables.
One of the challenges in subsea methane analysis is the need for highly sensitive instruments capable of distinguishing between different hydrocarbon gasses in a complex underwater environment. Advances in sensor technology, miniaturization, and energy efficiency continue to drive improvements in subsea methane detection.
The Importance of Methane Analyzers
Methane analyzers play a vital role in subsea applications, enabling precise monitoring and analysis of methane emissions. From environmental monitoring and scientific research to leak detection in the oil and gas industry, these instruments are essential for both protecting the marine environment and advancing our understanding of the deep ocean.
Products (3)
Related Articles

High-Accuracy Dissolved Gas Sensors for Oceanography, Environmental Monitoring, and Oil & Gas Applications

Marine Monitoring Systems for Surface & Underwater Vessels | Advanced Power Solutions for Subsea Vehicles