Suppliers
Add your company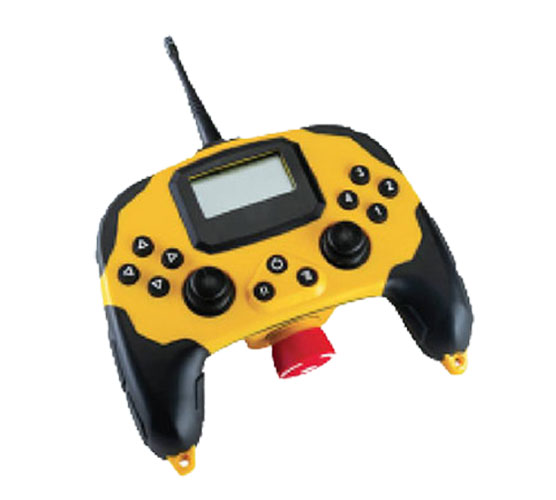
AI-Powered Maritime Autonomy & Remote Control Solutions for Government & Commercial Vessels

Marine Vehicle Management Technologies: Marine Autopilots, Remote Control Systems, and Simulation Solutions
If you design, build or supply Handheld Controllers, create a profile to showcase your capabilities on this page
Products
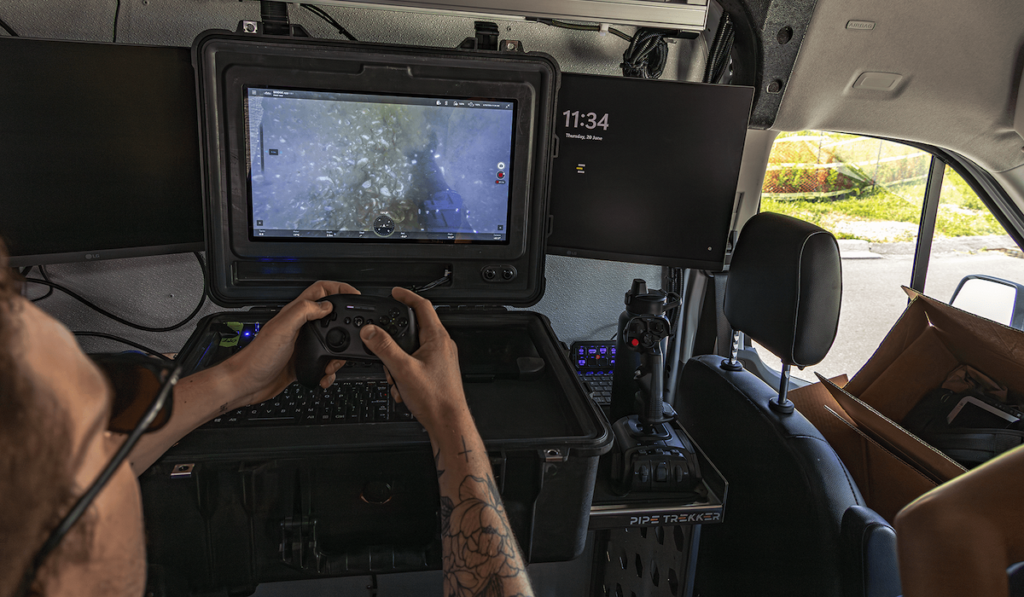
Handheld Controllers for ROVs & Unmanned Marine Systems
Handheld controllers designed for ROVs, UUVs, and USVs serve as critical tools for mission execution in underwater and surface environments. Engineered for mobility, ruggedness, and precision, these control interfaces support tasks ranging from offshore ROV inspections and environmental monitoring to military surveillance and confined space exploration. Integrated with joysticks, touchscreens, inertial sensors, and multi-port connectivity, modern handheld controllers enable remote piloting with tactile precision and situational awareness. Their ergonomic design allows operators to perform intricate maneuvers under challenging marine conditions without bulky control stations.
Handheld Controllers for Uncrewed Marine Vehicles
Handheld controllers are portable, often ruggedized devices that enable manual operation of unmanned marine systems. Unlike stationary consoles or rack-mounted units, handheld controllers are optimized for flexibility in the field. These devices interface with an array of marine platforms, including:
- Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs): tethered underwater vehicles commonly used for inspection, research, and recovery
- Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs): untethered or autonomous underwater systems for reconnaissance, survey, and data collection
- Unmanned Surface Vehicles (USVs): surface vessels used in hydrographic mapping, patrol, and surveillance
Equipped with joysticks, switches, LCD or color screens, and USB or HDMI ports, these controllers facilitate real-time feedback and manipulation of vehicle systems, sensors, and payloads. Many units include built-in displays or HUD overlays for enhanced situational awareness in harsh marine environments.
Applications Across Ocean Science & Technology
Handheld controllers are deployed across various oceanic applications, supporting scientific, commercial, and military missions:
Scientific Research
Controllers are used in marine biology and environmental monitoring missions to operate ROVs and UUVs for seafloor mapping, coral reef studies, and water quality sampling. With features such as IMUs and HUD overlays, researchers can maintain precise vehicle orientation and record measurements efficiently.
Offshore and Subsea Operations
In pipeline inspection, tank inspection, and offshore asset monitoring, handheld controllers provide the responsive control required to guide ROVs through confined and complex structures. Waterproof housings and ergonomic designs ensure reliability during long-duration operations.
Search and Recovery
During underwater inspections or post-incident recovery operations, operators use handheld units to navigate tight spaces and retrieve objects. Rugged casings, integrated pushbuttons, and micro joysticks support high-precision tasks in low-visibility environments.
Defense and Security
Military forces utilize handheld controllers in mine countermeasure operations, harbor patrol, and hull inspections. These units are often compliant with MIL-STD specifications and designed to function in electromagnetic and shock-prone environments.
Key Features of Modern Handheld Controllers
Technological advancements have enabled significant enhancements in the design and functionality of handheld marine controllers:
- Joysticks and Micro Joysticks: Enable proportional control of thrusters and manipulators
- Touchscreens and LCD Screens: Provide interface access to telemetry, camera feeds, and diagnostic data
- Connectivity Modules: Allow USB ports, HDMI ports, and Ethernet ports for interfacing with multiple systems
- Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs): Assist in stabilization and orientation tracking
- Pushbuttons and Rotary Switches: Offer programmable inputs for rapid command execution
- Rugged Housing: Waterproof, corrosion-resistant designs for subsea environments
- Built-In Displays and HUD Overlays: Improve visibility of navigation and sensor data in real time
- Battery Systems: Ensure extended operational time without dependence on tethered power
- Expansion Bays: Support add-on modules such as wireless transmitters or custom interfaces
Types and Models of Handheld Controllers
Handheld controllers for ROVs, UUVs, and USVs vary based on platform type, mission duration, and environmental conditions. Common classifications include:
- Basic Gamepad-Style Controllers: Ideal for entry-level applications or training simulators. Often modeled after gaming consoles with USB connectivity.
- Ruggedized Marine Controllers: Designed for field deployment, with sealed casings and integrated inertial sensors.
- Integrated Display Controllers: Include built-in LCD or color screens to monitor video streams and telemetry.
- Customizable Modular Units: Allow expansion with HUD overlays, IMU integration, or multiple joystick configurations.
- Wireless Handheld Controllers: Provide freedom of movement during topside operations on vessels or platforms.
Comparisons with Other Control Interfaces
Compared to stationary surface control stations or PC-based workstations, handheld controllers offer several advantages:
| Feature | Handheld Controllers | Stationary Consoles |
| Portability | High | Low |
| Ease of Use | Moderate to High | High |
| Environmental Resistance | High (when ruggedized) | Moderate |
| Power Requirements | Battery or USB | External power source |
| Screen Integration | Optional | Standard |
| Joystick Configuration | Modular | Fixed |
While consoles offer enhanced visualization and multi-system control, handheld units are preferred for quick deployment, confined space inspections, or field-based missions requiring mobility.
Standards & Environmental Compliance
Handheld controllers used in highly-regulated industries and military applications often adhere to the following standards and design criteria:
- MIL-STD-810: Governs ruggedness, including resistance to shock, vibration, temperature, and moisture
- IP Ratings: Ingress protection ratings indicating dust and waterproofing levels, often IP67 or higher
- EMC Compliance: Ensures electromagnetic compatibility in sensitive naval environments
- ISO 13628-6: Standards for subsea production systems, which inform some controller specifications for underwater tooling and operations
- STANAGs (NATO): May apply to defense-specific controllers for interoperability across allied forces
These standards ensure controllers operate reliably under demanding conditions such as saltwater exposure, pressure changes, and electromagnetic interference.
Design Considerations for Field Use
To support operations in remote or offshore environments, handheld controllers incorporate design elements that enhance user experience and reliability:
- Ergonomic Grips: Reduce operator fatigue during extended missions
- Backlit Buttons and Screens: Support usability in low-light or subsea conditions
- Cable Management: Secure and durable cable connections for HDMI, USB, and Ethernet ports
- Battery Life: Extended runtimes and hot-swappable battery packs to avoid downtime
- Durable Materials: Use of corrosion-resistant alloys, waterproof seals, and reinforced switches
- Fast Boot and Reconnect Times: Ensure minimal delay in mission-critical situations
Future Trends in Handheld Marine Controllers
Innovation continues to shape the evolution of marine handheld controllers. Emerging trends include:
- Haptic Feedback Systems: Providing tactile responses based on sensor inputs or collision detection
- Advanced Wireless Modules: Enabling encrypted, low-latency communication with unmanned platforms
- Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: Overlaying navigation or mission data onto the display
- AI-Based Controls: Predictive joystick behavior and object-following capabilities
- Cloud Sync and Data Logging: Real-time upload of mission data and diagnostics
These advancements aim to increase operator efficiency, safety, and mission flexibility in real-world conditions.